Artificial intelligence’s growth has been exponential in all industries. Many believe AI’s capabilities has just scratched the surface. For architecture and STEM-related industries, this is an exciting and daunting prospect.
In this article, we will try to give you a rounded view of how artificial intelligence is changing the architectural industry and the built environment by association. It’s important to understand that AI will have important implications within the industry, whether this is seen as positive or negative.
HOW IS ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE BEING UTILISED?
A survey conducted by Enscape tells us that over 60% of all architects use AI in some form. Out of those surveyed, roughly 40% of architects have had some form of training, or are in the process of training with artificial intelligence. From these stats alone it’s clear that AI has a future in architecture.
Out of those currently using AI, how are they doing it? It’s important to note that there will be a huge disparity between the uses of one architect to another. Daily use of AI may include search optimisation such as ChatGPT and scale up to less frequent but more detailed uses such as Text-to-Bim
- Design Support: AI assists architects in generating design alternatives and exploring innovative solutions. By analysing a wealth of data, including building codes, site conditions, and client preferences, these algorithms can suggest design options tailored to specific requirements.
- Design Generation: AI algorithms enable the generation of multiple design options based on set parameters, allowing architects to explore a diverse range of possibilities. This process aids in optimising designs, enhancing efficiency, and uncovering solutions that may not have otherwise been considered
- Enhancing Energy Efficiency and Sustainability: AI plays a significant role in promoting energy-efficient and sustainable building design by analysing data and simulating performance. Through this analysis, AI can pinpoint areas for enhancement, optimise building systems, and improve energy consumption predictions.
- Advancements in Building Information Modeling (BIM): AI enhances BIM software capabilities by automatically analysing and extracting information from scanned drawings and images. This streamlines the data entry process, reducing time and human error whilst improving the overall accuracy of the model. As mentioned above, new technologies like Text-To-BIM have been introduced to some markets.
- Immersive Experiences through Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): AI-driven algorithms create real-time, interactive experiences in VR and AR environments. This enables architects and clients to visualise designs before construction, fostering better understanding and facilitating informed decision-making throughout the design journey.
- Streamlining Construction Processes: AI technologies like computer vision and robotics can automate various construction tasks, including site monitoring, quality control, and even safety inspections. This automation enhances productivity on construction sites and helps reduce errors, ultimately improving the efficiency of construction processes. Currently, most of the steps are double-checked by humans.

WHAT ARE THE CONCERNS OF AI IN ARCHITECTURE?
New technologies, services and methods come with their risks. AI, however, poses a new challenge on many fronts. The implications of using artificial intelligence in architecture will have long-term effects. It’s therefore important we highlight and resolve potential issues now before completing the integration of daily work.
So just what are the concerns?
- Ethical and Social Implications: When incorporating AI in architecture, it’s essential to consider the ethical implications, including data privacy, algorithm bias (including limited or skewed data), and societal impact. Architects are urged to prioritise transparency and ethical AI practices, fostering trust with clients and fellow architects.
- Data Security: Safeguarding the confidentiality and security of data is of utmost importance when utilising AI in architecture. Architects must now think and implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive information.
- Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with regulations and standards concerning AI usage, data management, and privacy is crucial. Architects must stay informed about pertinent laws and guidelines to ensure legal compliance and ethical conduct.
- Lack of Skills: Given the continuous evolution of artificial intelligence, architects need to continually enhance their skills and knowledge to effectively harness the potential of AI tools. Training and upskilling in AI applications will be costly essentials for professionals to leverage these technologies to their fullest capacity. If done incorrectly, this has the potential to lose money and reputation.
- Loss of Creativity: Architects should approach AI as a collaborative tool, complementing human creativity and expertise rather than replacing it. Fostering an understanding of how to work alongside AI systems effectively can lead to improved design outcomes and efficiency.
- Financial and Resource Considerations: Integration of AI technology in architecture will likely include financial investment in software, hardware, and training. Architects should thoroughly evaluate the costs and resources involved to ensure a positive return on investment.
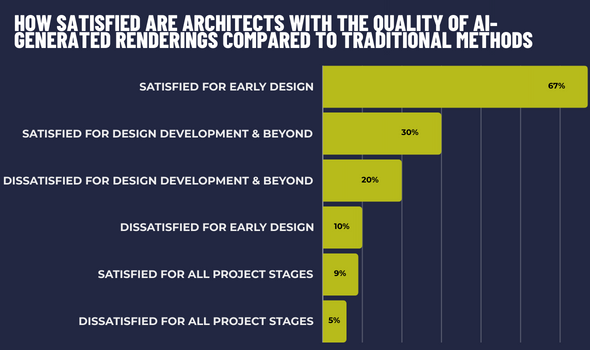
CONCLUSION
Predicting how much AI will impact the architectural industry moving forward is nearly impossible. However, it’s clear artificial intelligence is helping shape the architecture industry, and we’ve only just scratched the surface! Considerations including copyrighting, impacts on existing contracts and how to price fairly are just a few examples of immediate implications. This is backed up by Enscapes survey with 74% agreeing ethical guidelines are needed.
Architectural design and human innovation is what makes many of our buildings stand out. As technology increases it’s clear the relationship between AI and architecture will also. It’s also clear better training and understanding is needed.
Collaboration is a word used so often within STEM industries and its relevance here is paramount. We must find a balance between the use of artificial intelligence and personal creativity to ensure our built environment is both practical and aesthetically pleasing.
Our survey work at Spatial Dimensions has also seen the introduction of AI in defined roles. Specifically, artificial intelligence has seen mass improvements in the use of BIM and drone surveying which can feed into architectural clients, saving them time and money. You can read more about the role of AI in surveying and its defined roles here. As with architecture, AI within surveying has only just begun. As one of the UK’s leading measured survey companies, we understand the importance of embracing technology whilst contemplating and resolving any potential issues for our clients.


